Proof A: The Living Average & Directional written in terms of K, the Scaling Factor
![]()
![]()
Proof B: Number String's Living Average & Directional for the 1st point (N=1)
![]()
![]()
Proof C: Number String's Living Average & Directional for the 2nd point (N=2)
![]()
![]()
Proof D: Number String's Living Average & Directional for the 3rd point (N=3)
![]()
![]()
Proof E: General Expression – Number String's Living Average
Theorem E is the formula for the Number String’s Living Average, the 1st derivative.
"Induction Principle. A statement Q(n) about the integer n is true for all positive integers n if
1. Q(1) is true.
2. For each integer n, the truth of Q(n) implies the truth of Q(n+1); that is, if Q(n) is true then Q(n+1) is true.
The truth of Q(n) is often called the induction hypothesis, since it is the hypothesis of the implication of property 2." (Burton W. Jones, An Introduction to Modern Algebra, 1975, p. 132)
Proof F: General Expression – Number String's 1st Directional
Theorem F is the formula for the Number String’s 1st Directional, the 2nd derivative.
![]()
Proof G: Supplementary Proof - the Middle Term
![]()
Proof H: Number String's Living Average & Directional when A = 1
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Proof I. The Living Average's Limit = the Number String's Content, A.
A common calculus theorem states that:
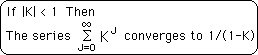
![]()
Theorem I: As N, the number of Living Algorithm iterations, increases, the Number String's Living Average approaches A, the Number String's content.
![]()
Proof J. The Limit of the Number String's 1st Directional = 0.
![]()
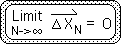
Proof K. The Limit of the Number String's 2nd Directional = 0.
Theorem K: As N, the number of Living Algorithm iterations increases, the Number String's 2nd Directional approaches 0 as a limit.
![]()
Proof L. The Change Series written in terms of the Directionals & the Data
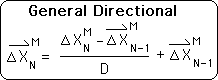
![]()
Theorem L: The Change Series written in terms of the Directionals & the Data
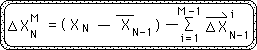
Proof M. An Alternate General Expression for the Mth Directional
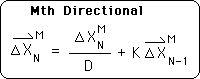
![]()
Theorem M: an alternate expression for the Mth Directional.
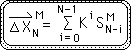
Proof N. The Limit of the Number String's Directionals = 0.
Theorem N: as N approaches infinity, all the Number String's Directionals approach 0.
![]()
Proof O. The Number String's Directionals = Number String Content * Constant
![]()
![]()
Theorem O: All Directionals of the Number String Data Stream equal the product of the Number String's Content, A, and a constant, C, which is a function of D, the Decay Factor.
![]()